Even though the history of e-commerce began in the 1960s, it has undergone global changes mainly during the last two decades. E-commerce involves e-information exchange, e-capital flow, e-transaction, e-marketing, e-banking and e-insurance services[1]. The development of e-commerce is quite fast and intensive nowadays. The buyers’ wish to save time and money leads to businessmen’s need to use Information Technology’s achievements. E-commerce is a means of carrying out business internationally and the pace of its implementation and the results show the preconditions of a radical change in sales and purchasing system and a shift to a global level in trade. The rapid development of this type of trading became possible only after the popularization of Internet[2].
Online trading has now become an inseparable part of the global economy. But the development of this direction has different paces in various regions. The absolute leader in the field of e-commerce is the Asia-Pacific region. In terms of e-commerce, here it develops two times faster than in Northern America (mainly due to China). This tendency is conditioned by numerous circumstances, especially by the demographic factor and the continuous growth of Internet availability[3]. The high growth rate of China’s economy in the last few years, as well as expert forecasts for its maintenance and further development prove that it is to some extent linked to China’s leading position in the global e-commerce sector.
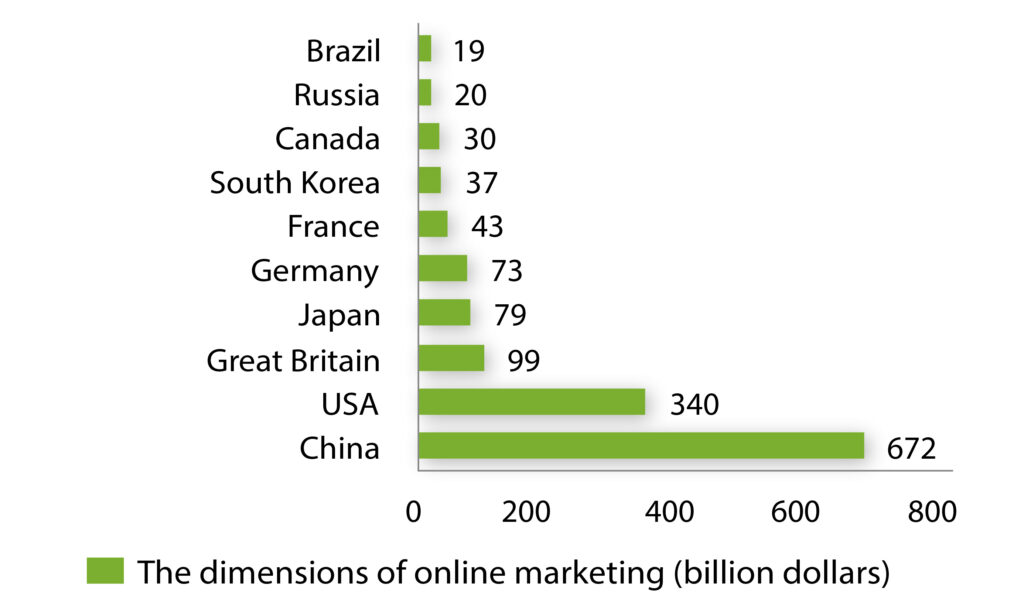
When presenting the dynamics of e-commerce, it is necessary to consider the general global trend of digitalization of society to reduce the expenses as much as possible regarding the considerable part of transactions if they can be implemented on electronic platforms. By 2023, online retail sales were predicted to reach $ 6.5 trillion, but the present predictions have been undergoing changes since the pandemic outbreak.
According to Eurostat’s data for the end of 2019, the centre of e-commerce in Europe is Great Britain. The online sales here are three times higher than in Germany- Europe’s second largest market. The dominant site in Great Britain is Amazon, which accounts for 54% of total sales. In Europe, 81.5% of e-commerce accounts for only three countries: Great Britain, Germany, and France. Moreover, they show a persistent growth of this indicator year after year[5].
At the moment, there are a number of problems in the e-commerce market that prevent development and may lead to unrealistic predictions by experts. The following issues need to be solved in the online retail market:
- Ensure a high percentage of accessible internet available to the public.Improve the conditions of providing buyer’s personal data security and the terms of returning goods and money.
Although in the conditions of modern market economy an attempt is made to reduce the level of state intervention in economy as much as possible, it should be noted that the regulation of economy and e-commerce as its constituent part, as well as the solution of the problems in the sphere, are possible only in cooperation with the state. The state should participate in the solution of the above-mentioned problems not directly but by adopting laws and sub-legislative acts, while their application should ensure the systematic and full implementation of measures taken by the market subjects to address these issues. The customers, in their turn, need to be able to master the skills of using the networking toolkit and develop the culture of online purchase[6].
When talking about the dynamics of e-commerce, it is important to consider the current situation in the global economy, as it is a new impetus for the growth of e-commerce. The problem is that the need of keeping social distance makes people stay at home and shop online, but there is also the following problem: the longer people stay at home and lose the opportunity of earning extra money, the more it leads to the preference changes towards separate segments of e-commerce. Therefore, the dynamic growth in separate branches of e-commerce simultaneously results in reductions of trading volumes in the secondary units. Self-isolation and applying various economic restrictions would have been impossible at the beginning of the 2000s, but today we have the most crucial thing- the opportunity to shop from home.
Nowadays, the digital world changes faster than the real world. Even an e-commerce giant like Amazon intends to hire more employees to meet the USA’s steady increase of consumption demand. The consumers’ preferences also change depending on the pandemic. A survey conducted by Nielsen revealed the main changes in the consumers’ behaviour, such as food and household items, necessary disinfectant and hygiene products needed for protection against the virus and so on[8].
Alibaba was the first to react to the pandemic outbreak in China using its digital logistics platform. The country’s virus situation was the precondition which made them move the technological experiments, conducted in the field into real life thus reducing human movements as much as possible. As a result, they had an opportunity to meet the increasing demand without breaking restrictions enacted by the country.
In the second quarter of 2020, Amazon expects to invest around $ 4 billion for the expenses of COVID-19 to supply goods for its customers and ensure employee safety. In March and April, the company announced the necessity of involving new employees. Since then, it has hired 175.000 new employees in response to the continuous increase of customers’ demand[9]. The French and Italian online trading centres also prove the remarkable increase of e-commerce volumes in pandemic conditions[10].
According to the forecasts by GlobalData, the Chinese e-commerce market will continue to grow in the future, exceeding all the previous predictions[11].
Given that global output is declining overall, it’s not surprising that the macroeconomic indicators are slumping for most countries too. As e-commerce is the central area of growth in these conditions, GlobalData predicts that it will form a considerable part of GDP in the coming years. According to the assessment of the same center, the pandemic will significantly impact Italy, China and the USA as countries most affected by COVID-19.
To sum up, we want to remark that the main challenge for most e-commerce participants worldwide is the growing demands for a technological component of online shops, the necessity of comprehensive promotion and the security of the customers’ personal and payment data. Considering the situation in the international economy caused by COVID-19, we can say that due to the pandemic, the interest of the wide masses of public in online trade has considerably increased. Thus, the main task of the people involved in e-commerce has to be the diversification of customers. Using this information, the online trading centers can conduct personalized and targeted campaigns to meet the preferences of each group.
China’s experience suggests that the efficient usage of the e-commerce system is one of the most important ways of overcoming the pandemic by engaging citizens who have lost their jobs on digital logistic platforms, advanced technology and other areas. In this situation, the economist entities’ significant part of income is directed to the purchase of first necessity products, changing the structure of their consumption. However, it’s natural that after overcoming the pandemic, the former structure of consumer demand will be restored in general. At the same time, the increase in e-commerce volumes becomes unavoidable. In pandemic conditions, the restrictions made the consumers implement the majority of their purchases and transactions on e-platforms, allowing them to discover and value the positive aspects of e-commerce that they had not previously appreciated. The proof of what we said is the constant pursuit of people’s comfort and online platforms provide the opportunity to get the necessary goods quickly and conveniently saving the most expensive resource-time. Therefore, those positive aspects of e-commerce become the preconditions that will determine its further growth even after overcoming the pandemic. However, as practice shows, the market, in cooperation with the state, successfully finds solution to all the problems that are in the process of its development, and the most effective solutions quickly become modern standards in the economy.
[1]Юрасов А.В. «Основы электронной коммерции», Горячая линия-Телеком, Москва, 2014. – 500с. [2]Климонова А.Н., Трибунская У.Г. Особенности и этапы развития электронного бизнеса в России // Социально-экономические явления и процессы. 2013. № 12 (058). https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/osobennosti-i-etapy-razvitiya-elektronnogo-biznesa-v-rossii/viewer [3]«J’sоn & Partners Consulting» https://json.tv/en/ict_telecom_analytics_view/technologies-equipment-and-services-for-mud-logging-in-russia-and-the-world [4]https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database [5]Statistical data of research agency «Remarkety» [An electronic resource] of URL: https://www.remarkety.com/global-ecommerce-sales-trends-and-statistics-2015 [6]Statistical data of the center of strategic researches of the Enter company [An electronic resource] of URL: http://www.towave.ru/pub/sovremennye-trendy-razvitiya-rynka-riteila-v-faktakh-i-tsifrakh.html [7]https://www.digitalcommerce360.com/2020/03/12/coronavirus-affects-online-retailers/ [8]https://internetretailing.net/views/editorial-the-corona-virus-budget-may-be-the-way-to-reset-retail [10]https://www.digitalcommerce360.com/2020/03/12/coronavirus-affects-online-retailers/ [11]https://www.globaldata.com/covid-19/References
Bibliography
Author: Narine Petrosyan. © All rights reserved
Translator: Jemma Khachatryan.