Recently, we often come across the terms “cryptocurrency” and “bitcoin.” Heated discussions concerning the spread of cryptocurrency and the change in its price still continue.
After all, what is cryptocurrency? And how is it made?
Cryptocurrency is a means of payment, the stocktaking of which is decentralized. It is an encrypted piece of information, which is impossible to copy (hence the term “crypto” is used in the name). The term “cryptocurrency” came into circulation after the article concerning bitcoin – a virtual currency and payment system. The concept was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto. Till now, his identity is not clear. Satoshi Nakamoto is more likely an individual or a group of individuals who use the given pseudonym. Nakamoto introduced the concept on 31 October, 2008, and it began spreading in 2009. A year after the creation of the project, Nakamoto left the concept and passed his authority to Gavin Andresen.
Bitcoin came into circulation with the price of only $1; however, after a short time, it established a record price, surpassing the amount of $5000. Cryptocurrencies are based upon the technology of blockchain.
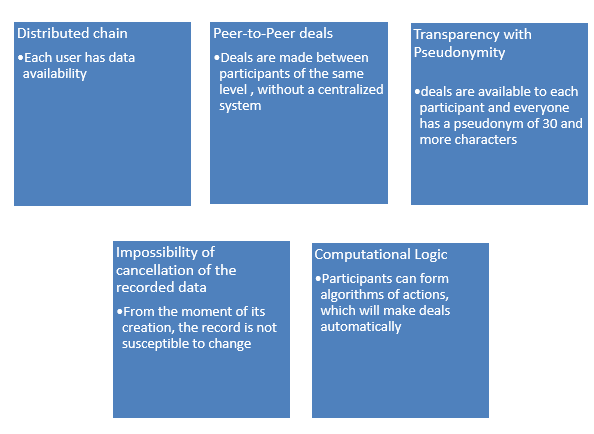
A blockchain is a decentralized, digitized, open access (public) ledger where all cryptocurrency transactions[i] are registered. The records about the transactions registered in the ledger are constantly added in chronological order, which allows the participants of the transaction to follow the execution of the transactions without centralized registration as each participant receives a copy of the blockchain, which is uploaded automatically.
Presently, this technology is mainly applied to follow and control cryptocurrency transactions, which is actualized by a so-called Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT). At the same time, it is possible to encode and include any kind of document in the blockchain. It is impossible to make changes in the downloaded unit, and all the participants can check its verity by using the blockchain instead of the centralized registration system.
A block is the ongoing part of the blockchain, which registers some or all the transactions. After completing the process of registration of a block, it is connected to the chain, which is a permanent data registration base. Once a block is over, a new one is created, which is chronologically connected to the block-chain. Each block contains the hash (hash – a cryptographic function of 256 bits[ii]) of the previous block. As a result, the blockchain contains the data of its users and information about their transactions from the initial block to the most recent one.
Blockchain is made in a way that the recorded data cannot be changed, and the information is not copied but distributed in the chain.
Thus, the technology of blockchain is based upon the following main principles[iii].
Description of Transactions
In his article, Satoshi Nakamoto defines electronic currency or coin as a chain of digital signatures [iv]. Each user makes additions to the chain via the function of encoding the previous transaction (hash function) and adds the public key of the next user appending to the end of the chain. The receiver of the transaction can check the electronic signatures to identify the transaction participants[v].
In case of wide use, cryptocurrencies can bring significant changes to the financial system. Due to the implementation of this innovation, the transactions will become quite easy, their fees will be reduced, and the time spent on them will be shortened, as well. Nevertheless, Eugene Kaspersky thinks that cryptocurrencies will work well only after 300 yearsvi.
One of the advantages of cryptocurrencies, as was mentioned, is the low price of transactions. Those transactions imply rather low fees, comprising 0-1% of the money transacted. For the comparison, we can mention that in the case of online payment systems, the above-mentioned fee comprises 2-4% of the money transacted, and in the case of using the services of money transfer companies – 8-9%.
The transactions of virtual cryptocurrency take place faster than those of real ones. In the case of bitcoins, the transaction may last from 10 to 60 minutes. We should also mention that cryptocurrency payments are made twenty-four-hour, without any time restrictions.
Another advantage is the controllable risk of inflation. Unlike cryptocurrencies, real currencies are greatly influenced by governments and central banks, which can also influence the money supply. In the case of virtual currencies, inflation may occur when, in a given condition of fixed supply, some cases of decrease of demand or growth of the supply of the offered bitcoin are observed.
Perhaps one of the greatest advantages is the fact that the transactions do not require personal data. A bitcoin user may protect his money via encryption. Unlike other means of payment, a hidden charge of money by traders is not possible.
Disadvantages:
-
- The prices can change drastically, and those changes are impossible to predict.
| From January to October, 2017 | During last 12 months | Average annual change since 2013 | |
| Bitcoin | +495% | +717% | +1010% |
| Ethereum | +4169% | +3016% | +2080% |
| S&P 500 | +14% | +20% | +13% |
| Gold | +13.5% | +11.5% | +4% |
The change in the price of cryptocurrencies in comparison with the change in the prices of the American S&P index fund and the price of gold [vii][viii]
2․ As there is no control, the cryptocurrencies can be used for criminal purposes, such as money laundering, tax evasion, and frauds like Ponzi scheme. Ponzi scheme is a fraudulent investment operation: the investors are promised high returns in low-risk conditions. Because of the lack of control, many can fall into the “trap.”
3․ There is a great probability of tax avoidance.
4․ The ubiquitous use of bitcoin will lead to a condition when demand exceeds supply, as a consequence of which its price will consistently grow. The prices of services and goods will decrease, and such a deflation in its turn will have a negative effect on the economic growth.
5․ Like any currency, bitcoin is also naturally attractive for thieves. Though few, some cases have been recorded anyway. In 2011, one of the users announced that 25000 bitcoins had been stolen from his “wallet.” And in 2015, it became known that 50000 bitcoins, nearly 230000 US dollars, had been stolen from the Webhost Company.
The Central Bank in Armenia exhorts to abstain from the usage of cryptocurrencies until the introduction of respective regulations[ix].
In the Russian Federation, they work on introducing specific mechanisms of control. The President of the Russian Federation states that the creation of specific mechanisms of control is essential for minimizing tax evasion, dirty money laundering, funding of terrorism and counterfeit. It is a grave danger in a state of absence of control.
The former chief economist of the International Monetary Fund, Kenneth Rogoff, predicts the downfall of bitcoin in the near future.
The President of the European Central Bank, Mario Draghi, has announced that only one currency can be circulated in the Eurozone, and the Eurozone countries cannot issue national currencies [x].
But in Japan, for instance, bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are officially considered means of payment.
We should mention that virtual currencies, including bitcoin, are not considered electronic money in Armenia.
Despite the noise it has made, cryptocurrency has many advantages that can be used for economic and business development. Naturally, it is too early to speak about the spread of bitcoin in Armenia. But as in other countries, in Armenia, too, the implementation of bitcoin will contribute to economic growth. The absence of control and shady deals are of considerable danger. The best way to secure the users from the risks is the increase of the role of the knowledge and the abolishment of information asymmetry. If during a transaction one party is more informed than the other, there is a great probability of deceiving. On the other hand, the possession of the respective information will prevent the loss of the means of payment.
[ii] But how does bitcoin actually work? [iii] The Truth About Blockchain [iv] “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” Satoshi Nakamoto, 2008․ [v] Dotted line – identification, broken line – signature, thick line – encoding (hashing)․ [vi] Kaspersky: the full potential of cryptocurrency will become available 300 years later [ix] What is cryptocurrency? Where are the risks? [x] Mario Draghi rejects suggestion of Estonian cryptocurrency․References
Authors: Lilit Ovsyan and Hakob Hakobyan © All rights are reserved.
Translator: Lilit Maghakyan․